Carotid artery
The carotid artery is one of the different arteries that supplies blood to the head and neck. Of the two common carotid arteries, which extend toward the head on either side of the neck, the left one originates in the arch of the aorta over the heart; and the right one originates in the brachiocephalic trunk, the largest branch of the arch of the aorta. Each common carotid artery is divided into an internal carotid artery and an external carotid artery.
What is the carotid artery?
It is one of the arteries of the human body whose function is the blood supply to the head and neck and that originates in the common carotid artery, when it branches into the external and internal carotid.
Function
The function of the external carotid arteries is to supply oxygenated blood to the head region. There is an external carotid artery on the right side of the neck and another on the left side of the neck. The common carotid artery is located bilaterally, with one artery on each side of the front of the neck. Each common carotid artery is divided into an external and internal carotid artery. These arteries carry blood to structures inside and outside the skull. The external artery carries blood to the external structures located in the skull, mainly the face, and the internal artery to the internal structures of the skull, including the brain.
Location
The external carotid artery is born at the junction between the neck and the common carotid artery. It arises from the bifurcation of the common carotid, just at the top edge of the thyroid cartilage, at the level of the fourth cervical vertebra. The internal carotid artery is born at the angle of the mandible, from the right and left common carotid arteries, which bifurcate to shape these arteries. It ascends in front of the three upper cervical vertebrae and does not branch into the neck.
Left common carotid artery
This artery is a large vessel that comes from the aorta and is responsible for irrigating the neck and head. It is divided into two: common carotid artery right and left. The right common carotid artery comes from the arteriosus brachiocephalic trunk and rises to the top edge of the thyroid cartilage, where it divides into external carotid and internal carotid. The left common carotid artery, coming from the arch of the aorta, rises and ends in the same place, the thyroid cartilage, which is divided into the external and internal carotid.
Right common carotid artery
This artery is born at the bifurcation of the brachiocephalic trunk, next to the right subclavian artery. It is then directed vertically to the cervical region. Its origin is more in the internal part of the supraclavicular region.
Internal carotid artery
The internal has as function blood supply of the neck, the hemispheres of the brain, the eyeball and the structures that are annexed, including the frontal part and the root of the nose. It begins at the bifurcation of the common carotid, in the thyroid cartilage, and then enters through the carotid duct and ends up dividing into the anterior cerebral artery and the middle cerebral artery. It is divided into four parts:
- Cervical: The cervical portion does not have any branching and begins in the common carotid.
- Petrosa: Starts in front of the cochlea and the eardrum box. It is surrounded by the venous plexus and the external carotid plexus. It has two branches: the carotid tympanic branch, which enters the eardrum; and the pterygoid branch, which is inconstant and anastomose to the branch of the internal maxilla.
- Cavernous: Located in the cavernous sinus, it irrigates the common ocular motor, trochlear and ophthalmic nerves. It is divided into cavernous branches, which are small vessels that irrigate the trigeminal; hypophysial branches, which are small and are found in large numbers; and the meningeal branch, which is small and irrigates the dura mater and bones located in the anterior cerebral fossa.
- Cerebral: Passes between the optic nerve and the common ocular motor nerve. It is divided into anterior and middle It has several branches, among them: ophthalmic artery, anterior cerebral, posterior communicating, anterior choroid.
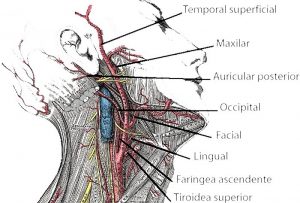
External carotid artery
It originates in the bifurcation of the primitive carotid artery, on the inner side of the carotid. It then ascends vertically out of the primitive carotid and up the neck. It passes through the styloid diaphragm and styloid ligament and then into the parotid gland. It ends in the thickness of the parotid gland. It presents the following collateral ramifications:
- Upper thyroid: originates in the bifurcation of the primitive carotid and goes up the head through the diaphragm.
- Lingual: originates in the external carotid above the lower thyroid. It is related to the pharynx and the floor of the mouth.
- Facial: born from the carotid and rises vertically to the submaxillary compartment. It passes through the pharynx.
- Ascending pharyngeal: it is born on the outside at the level of the tongue and ascends vertically over the pharynx.
- Occipital: originates in the external at the height of the face. It is related to the internal jugular, the internal carotid and the pharynx.
- Atrial: it is born in the external carotid and reaches the mastoid process. It is divided into parotid branches and mastoid-style artery.
- Parotid branches: they are born on the outside and vary in number.
In addition, it has two terminal branches: the superficial temporal arteries and the external maxilla.
Blockage of the carotid artery
A blockage occurs when one or both of the carotid arteries become narrow or clogged due to fat deposits that build up, a situation known as atheroma. When this obstruction is constant and untreated, strokes can occur, either from a blood clot or from the detachment of pieces of plaque. This risk increases with age and occurs more commonly in men than in women. It is considered the third cause of death worldwide. High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle and family history are the main risk factors.
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Carotid artery. Recovered on 3 January, 2025, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/carotid-artery/