Integer numbers
In mathematics, there are many types of numbers according to the characteristics they have. In this numerical typology, integers can be mentioned, which are those that do not have a decimal part and include natural numbers, zero and negative numbers. The notion of integers was established to refer to indivisible units such as a person or a country.
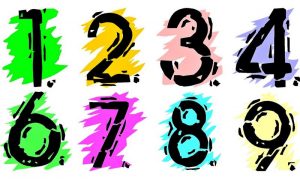
Related topics
Algebraic numbers, complex numbers, irrational numbers, prime numbers, rational numbers, real numbers
What are integer numbers?
Integer numbers are elements of a numerical set that groups natural numbers, their additive inverses, and zero. There are positive integers, negative integers, and zero. Indivisible units are represented and therefore, do not accept decimals. They are symbolized by the letter Z. They are represented on the number line by placing zero in the center of the line and from zero to the left, there is the progression of negative numbers and from zero to the right, the progression of positive numbers.
Which are the integer numbers?
Integers are: natural numbers, zero and negative numbers:
- Natural numbers are those used to count the elements of a set and to perform elementary calculation operations.
- Zero is a null value number that represents that there is no number or element to count.
- Negative numbers are those that result from subtracting a natural number with a greater one. Negative numbers are less than zero and represent losses, decreases, among other things.
What are integer numbers for?
Integers are used to express an accounting quantity, the absence of quantity and a negative quantity that can be the opposite of an amount or a debt.
Characteristics
Among the most outstanding characteristics of integer numbers, the following can be cited:
- They are made up of positive, negative and zero integers.
- They do not have decimals.
- The symbol that represents it is the letter Z.
- The zero is a number without value that divides the positive numbers from the negative ones. All numbers greater than zero are positive and all numbers less than zero are negative.
- Zero is considered a neutral number.
- They cannot be divided unless the division is exact.
- Positive numbers further from zero will represent more.
- On a number line, negative numbers are placed on the left, zero is placed in the center, and positive numbers are placed on the right.
History
The history of the integer numbers has a beginning in the epoch of the prehistoric man, who with his intellect was developing his capacity to count elements that were in the nature or in his mind. In the beginning, he made use of natural numbers, but with the passing of time these were not enough because he needed an element contrary to positive to express debts, or lack of whole elements (without decimals or incomplete). All this evolution of the uses and functions of positive and negative integers allowed man to generate several mathematical operations. In antiquity, specifically in the 3rd century B.C., in Mesopotamia, zero appears to refer to a null quantity or to something that has no value and that also marks the limit of negative numbers and the beginning of positive ones.
In the Middle Ages and modern times, the knowledge of these numbers and the operations that could be generated with them, served to develop many sciences that required mathematics such as architecture, medicine, economics and music among others. In the modern era, they were considered by their characteristics as part of rational numbers, which in turn are part of real numbers.
Nowadays, they are used in different simple and complex mathematical operations as in the commercial operations of our daily life, chemical formulas that look for accuracy or more complex equations than in other times. They are often used as meteorological indicators to indicate temperatures below or above zero. In this sense, it can be said that in man’s evolution, whole numbers have played a fundamental role in his logical-mathematical development.
How the integer numbers are represented?
They are symbolized by the letter Z which is the initial letter of the German word Zahien which means number.
The set of integers is usually represented by a number line divided by zero. This line starts from zero to the left with the negative numbers and from zero to the right with the positive numbers.
Properties
The properties of integer numbers are as follows:
Properties of integers as a set
Integers are an extension of natural numbers and are also a subset of rational numbers. These numbers are an indeterminate set since it is not known either beginning or end and its origin is zero.
They have their value determined in the position that they occupy in the numerical line.
Properties of integers in multiplication operations
The multiplication properties are:
- Associative (when factors multiply each other).
- Commutative (when the order of the factors does not alter the product).
- The neutral element that is the unit (any number multiplied by one does not alter the result).
- Distributive (when the factors are distributed in an equation, there are sums and multiplications).
Properties in addition operations
The addition properties are:
- Associative (summands association).
- Commutative (the summands can vary their order without altering the result).
- The neutral element is zero (any number added with zero does not change the result).
Operations of integers
With integer numbers, we can perform operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and powers between these numbers, but it can only be used in division when the quotient is also an integer.
Examples
Here are some examples of integer numbers.
Examples of positive integers
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
The number 1 is a neutral element in multiplication. Every number multiplied by 1 is equal to the number by which it is multiplied. Example 2×1=2
Examples of negative integers
-1,-2,-3,-4,-5,-6,-7,-8,-9
Example of integer 0
Zero is the neutral element in the sum. Any number added with zero is equal to the number being added. Example 5+0= 5
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Integer numbers. Recovered on 4 January, 2025, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/integer-numbers/