Limbic system
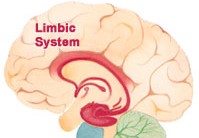
The limbic system is a complex set of structures located on both sides of the thalamus, just below the brain. It includes structures such as the hypothalamus, hippocampus, tonsils, and many other nearby areas. It is considered the main responsible for our emotional life, and has much to do with our memories, in addition it participates especially when it comes to behaviors that we need to develop for our survival such as feeding, reproduction and fight or flight responses.
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is a set of structures of the brain that are connected to each other and which has as a function the regulation of emotional states or instincts, is the center of all emotions, what we link with the irrational.
Characteristics of the limbic system
The main features of the limbic system are as follows:
- It is a neural network distributed throughout the brain and mixed with many different structures.
- It is related to emotional responses, learning and memory.
- The personality, memories and our way of being, depends to a great extent on the limbic system.
- It also intervenes in the creation of long-term memory.
- Regulate visceral activity and emotional response from sensory information.
- It regulates the character of individuals.
- It also acts on the peripheral nervous system.
- The word limbic has etymological root in the Latin word limbus which has as meaning “edge” or “limit”.
- It is the oldest part of the brain seen from the evolutionary point of view.
History of the limbic system
The first time the term was used was in 1878 by the doctor Paul Broca who used it to refer to an area located at the bottom edge of the pineal area. In 1890, Henry Turner called the parts of the limbic system as the nasal encephalon and later, in 1937, James Papez included more structures and even introduced the term limbic brain.
The concept of the limbic system was finally expanded by scientists such as Goldar, Heimer and Nauta. In psychology, during the twentieth century, the system has been considered as the subconscious and thinking system of the human being.
Location
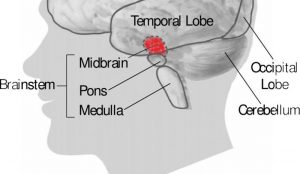
The limbic system can be found deep within the brain, below the cerebral cortex and on the brain stem.
Parts
The parts of the limbic system are as follows:
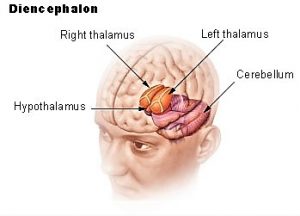
- Hypothalamus: is an area located in the diencephalon and is closely related to the regulation of our emotions and endocrine
- Hippocampus: actively participates in mind processes that are related to memory, experience and memory It is located on the inner side of the temporal lobes near the thalamus and tonsils. The hippocampus is a site in the brain where new neurons are created from adult stem cells, a process known as neurogenesis.
- Amygdala: they are located on the sides of the hippocampus; this means that we have one in each of the hemispheres of the brain. It intervenes in the emotional responses that are learned when we face a certain situation and participate in the learning of emotions.
- Frontal orbital cortex: it is a valve that allows the exit of the emotions towards the different zones of the frontal lobe. It intervenes in diminishing the impulses considered irrational that manage to reach the limbic system. It participates in the taking of actions to achieve medium- or long-term goals.
Functions
The limbic system is responsible for creating autonomous responses and emotions. It intervenes in the creation of responses to situations that are considered as threats by increasing heart rate, breathing and blood pressure. Participates in the creation of fear response by stimulating the hypothalamus and amygdala.
Another of its functions is the participation in the creation of the emotional memory, in the acquisition, maintenance and elimination of phobias and to facilitate us the survival, it also regulates the behaviors to feed and the appetite, and the olfactory system of the human body.
Diseases of the limbic system
Some of the diseases that can occur in the limbic system are the following:
- Dementia: it is related to the appearance of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Pick’s When the system is atrophied or damaged, especially the hippocampus, senile plaques begin to develop and the body’s ability to control movement is impaired.
- Anxiety: arises as a result of difficulties in regulating activity in the tonsils.
- Epilepsy: is a direct consequence of affecting the limbic system. The most common type that occurs in adults is temporal lobe epilepsy and arises when sclerosis occurs in the hippocampus.
- Affective disorders: Bipolarity and depression are diseases that are characteristic of damage to the limbic system, problems with emotional integration and learning, as well as problems controlling emotions.
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Limbic system. Recovered on 3 January, 2025, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/limbic-system/