Nematodes
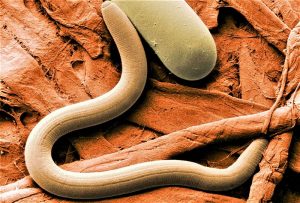
Round worms, which can also be called nematodes, are a species of worms that have a long, round body. They are worms that can vary in length from several millimeters to two meters. Round worms are common to be found in warm tropical countries. Children are more often affected than adults. Treatment is usually very effective but eliminating intestinal worm infections is always a fairly difficult process.
What are nematodes?
Nematodes are organisms that live in water, although they can also live on the surface. They are nemathelminth worms that have a digestive system that occupies most of your body.
Characteristics of nematodes
The most outstanding characteristics of nematodes are the following:
- They consist of a cavity filled with pseudo celomic fluid that surrounds the individual’s organs.
- They have a complete digestive tract with mouth and anus.
- Their body is elongated and cylindrical and they have good bilateral symmetry.
- They can live in any ecosystem and are the most abundant animals on Earth.
- They can be found in saltwater, fresh water, in the earth, in tropical regions, polar and even in high mountains.
- Most are parasitic, including a large number of species pathogenic to humans.
- Their usual size ranges from 0.1 mm to 2.5 mm in length and between 5 and 100 micrometers thick.
- Their head can be differentiated from the rest of the body and they have sensory hairs.
- Its surface is quite resistant and is called cuticle.
- The interior of the animal is composed of a liquid that serves as a hydrostatic skeleton and allows the distribution of nutrients.
Classification of nematodes
Nematodes can be classified as follows, according to the different investigations carried out on them:
- Secernataeum: This group of nematodes includes some species of round worms, usually living on land. Males have only one testicle and the reproductive system is tubular.
- Chromadorea: they inhabit marine sediments more regularly. They have a more sophisticated pharynx than other nematodes. They have ring structures in their bodies and also have three esophageal glands.
- Monhysteride: they have a funnel shaped pores to exchange gases and may have different types of teeth, which they can actually pull out.
- Dorylaimida: they live in humid soils, near the roots of plants. Many of them feed on bacteria or other microorganisms. They can also parasitize plants and fungi.
- Enoplea: your esophagus is cylindrical or bottle-shaped. They are smooth, and some have fine lines in their bodies. Their excretory system is simpler than that of other nematode groups.
Structure
These worms are cylindrical and long in shape, with bilateral symmetry. Their internal structure is relatively simple and consists of an internal intestine and an external muscular wall, which are separated by a pseudo cell, which is a cavity that is filled with fluid. Their length varies from microscopic to 10 cm.
In the wall of their body, we can find a cuticle covered with collagen for protection, an epidermis that can be cellular or syncytial where the excretory ducts are located, a basal membrane and a lot of musculature below the epidermis that connect the nervous system with the muscular arms; finally, they have a pseudocoeloms of reproductive organs that functions as a type of skeleton.
Nutrition
Nematodes can be fed with different types of materials. They can eat mushrooms, algae, some animals that are very small in size, they are scavengers so they can eat fecal material and remains of other animals and insects.
Reproduction
The reproduction of these animals is done through parthenogenesis, however, most of the time they do it sexually. It is quite common to be able to distinguish the sex of nematodes, although some species are hermaphrodites. During sexual intercourse, the male extends a spicule from his mouth and enters the female’s genital pore. When females become pregnant, they can gestate hundreds of offspring by means of eggs.
Breathing
Nematodes do not have any type of established respiratory organs and adults who have managed to position themselves and live as intestinal parasites are anaerobic, so they do not need oxygen, however, if oxygen is present they use it.
Circulation
Nematodes do not have any type of circulatory or vascular system. Nutrients travel through the pseudocoeloms which is driven by body movements and locomotion.
Nervous system
They have a ring of nerves located around the pharynx and from it arise different nervous ramifications. They also have sensory papillae, photoreceptor organs, and some have nerve and sensory glands.
Diseases caused by nematodes
Some of the diseases caused by nematodes are as follows:
- Ascariasis: is caused by contamination with human feces. Children are the most prone. The eggs of the nematode lodge in the small intestine invading the blood vessels of the mucosa and affecting the liver and lungs. It produces pneumonia, asthma and urticaria.
- Hookworm: it occurs mainly in humid and warm soils due to fecal contamination. It affects the lungs and the gastrointestinal system.
- Strongyloidiasis: they produce erythema pruriginosus and reach the lungs and small intestine where they become adult larvae. They produce diarrhea, encephalopathy, edema, hepatomegaly and paralytic ileus.
Nematodes in plants
The most common are, for example: Meloidogyne sp., Pratylenchus sp., Ditylenchus sp., Heterodera sp., Tylenchus sp. (in fruit trees). They damage the roots of plants and occur in greater quantities in sandy, hot and abundantly irrigated soils. They are sensitive to drought and cannot live without vegetation. In general, the plants lose their color or acquire a yellow tone, are malnourished and do not develop properly.
Beneficial nematodes
Some nematodes are not completely harmful, for example, worms help eliminate insect pests that are in the soil where crops are planted because they have a bacterium that can kill insects in as little as 48 hours. They do not affect humans and can eliminate weevils, fungi, mosquitoes, soil flies, some other types of worms and fleas.
Examples
The nematode species are:
- Adenophorea as enoplida, isolaimida and troplonchida.
- Chromadoria: araeolaimide, desmodoride and monhysteride.
- Secernentea: like spirurida, ascaridida and camallanida.
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Nematodes. Recovered on 3 January, 2025, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/nematodes/