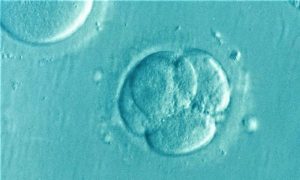
Ontogeny
Ontogenesis is the process by which an organism manages to develop its form. It is one of the most important aspects of biological development for living beings, along with cell growth and development and cell differentiation. It is a process that is in charge of controlling the cells in their embryonic process, although it can also take place in adults cultivating new cells, for example, when a tumor is born. It broadly describes the way in which an organism develops, from the time of zygote fertilization in sexual reproduction, until it reaches its adult form.
What is ontogeny?
Ontogeny is the process by which an organism achieves its form. It is the biological development of a living being in conjunction with its cellular development. It describes the way in which a living being develops from the moment the zygote is fertilized until it reaches adulthood.
We must remember that the concept is based mainly on the embryonic stage of both humans and animals. Thanks to ontogeny we are able to study the differences and similarities of the DNA chains in different species, and the changes it undergoes with time. It is useful to know the evolution process in species, families and different genera, and allows us to advance in different areas, such as, for example, searching for answers and solutions to the different mutations that sometimes occur.
Etymology
The word ontogenia can also be found as ontogenesis and refers to the process in which a being is produced or generated. The word is derived from a neologism dating back to the 19th century. This term is formed by roots of Greek words and is formed by the prefix onto and the suffix genia, which written in Greek are represented as follows: ὄντος whose pronunciation is ontos, and which has the meaning “to be, entity”. And the other Greek root is: γένεια, which is pronounced géneia, and which means “origin”.
What does ontogeny study?
Ontogeny, from the biological point of view, is the conformation and development that a person may have, mainly during the fetus’ embryonic stage. It is thanks to it that human beings have the ability to develop, from the time the egg has been fertilized until it leads to aging. It also studies the phases included within the same branch; the fertilization phase, in which the gametes are able to unite giving form to the zygote; the activation phase, which involves a large series of events after the zygote has already been formed and those that will give rise to the segmentation of the zygote; the embryogenesis phase, which refers to the process during which the zygote is divided into parts until it reaches the fourth phase, known as organogenesis. Through it, we can understand how an organism develops and how it changes its structure, we can observe how different types of cells in the human body are organized and the way in which the species is given continuity.
Human ontogeny
It is responsible for studying the extensive path that human beings travel to achieve physical fullness and the evolution of the species. It is the study of human development until death, distinguishing three different periods: development, maturity of the individual and involution. It is important to study each of these periods, since there are different biological and environmental factors that can affect and intervene in the evolution of man’s existence. These growth processes happen continuously through a large number of phases.
Animal ontogeny
Animal ontogeny is based on the study of morphological and functional development of animal species. Always based on embryos, it studies animals from birth until they reach a mature and adult state. As in humans, it studies the development since the ovum is fertilized.
Sleep ontogeny
Sleep ontogeny explains the different sleep stages in human beings. The sleep stages begin to emerge in babies even before birth, during the sixth and seventh month, fetuses begin to experience REM sleep and is closely linked to the development and maturity of the Central Nervous System. REM sleep in children is very active and has no relationship with watchful behavior.
Language ontogeny
Language ontogeny is responsible for studying and describing the child’s entire language process during early stages of life. This type of development has a biological origin and is based on stages that overlap each other. It is also linked to the learning process that the child acquires at the moment he or she begins to interact with the environment.
Nervous system ontogeny
It studies the development of the nervous system of the embryo since fertilization. It refers specifically to three different layers that are formed during this process. Around the third week of gestation, three important layers are formed, the endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. At the end of cell division, neurons emerge.
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Ontogeny. Recovered on 4 January, 2025, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/ontogeny/